Introduction:
Mechanical design engineering is a specialized field that requires a unique set of skills and knowledge. Whether you aspire to become a mechanical design engineer or are already on the path and want to enhance your capabilities, mastering specific skills is crucial for success. This article will explore the ten essential skills every mechanical engineer should focus on to excel in the mechanical design engineer role. From technical proficiency and CAD expertise to creativity and problem-solving abilities, let’s dive into the key areas that will set you on the path to becoming a skilled mechanical design engineer.
How to Become a Mechanical Design Engineer in 24 Weeks – A step-by-step Guide is available, at the end of this article.
Table of Contents
01) Technical Proficiency:
Technical proficiency forms the foundation of mechanical design engineering. It deeply explains core mechanical engineering principles, theories, and calculations. A solid grasp of engineering mechanics, strength of materials, machine design, machine drawing, manufacturing processes, materials science, and structural analysis is essential. It allows design engineers to apply fundamental principles in creating innovative and functional designs. Continuously expanding your technical knowledge base and staying updated with the latest advancements in the field will ensure your proficiency as a mechanical design engineer.
02) CAD and 3D Modeling & Drafting:
Proficiency in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software and 3D modeling tools is paramount for mechanical design engineers. CAD software such as Fusion 360, SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or CATIA enables engineers to create detailed and accurate designs, visualize concepts, and simulate performance. Mastering 3D modeling techniques empowers engineers to bring their ideas to life, analyze form and fit, and optimize designs before manufacturing. In addition, the ability to effectively navigate and leverage CAD software streamlines the design process, enhances collaboration with multidisciplinary teams, and accelerates product development timelines.
03) Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
GD&T, which stands for Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, is a crucial skill for mechanical design engineers. GD&T is a standardized language used to communicate design specifications and tolerances on engineering drawings. It allows engineers to precisely define the form, orientation, and location of features in a design, ensuring that parts are manufactured and assembled accurately. Proficiency in GD&T enables design engineers to convey precise requirements to manufacturing teams, reducing ambiguity and ensuring consistent quality. By understanding and applying GD&T principles, mechanical design engineers can enhance their designs’ functionality, interchangeability, and manufacturability, leading to more efficient and reliable products.
04) Knowledge of Materials and Manufacturing Processes:
Proficiency in materials science and an understanding of manufacturing processes are crucial for mechanical design engineers. Knowledge of different materials, properties, and behaviors empowers engineers to select the most suitable material for a given application. Understanding manufacturing processes such as machining, casting, forging, and additive manufacturing allows design engineers to optimize designs for ease of manufacturing, cost-effectiveness, and quality control. A deep understanding of materials and manufacturing processes facilitates the creation of functional and efficient designs to produce and maintain.
05) Mechanical Systems Integration:
Mechanical design engineers often work on complex systems that require the integration of various components and subsystems. Proficiency in mechanical systems integration involves understanding how different parts interact, ensuring proper assembly and functionality, and optimizing the overall system performance. Mechanical design engineers must have a holistic perspective and the ability to coordinate the integration of mechanical, electrical, and control systems. This skill ensures the final product’s seamless operation, compatibility, and efficiency. By mastering mechanical systems integration, design engineers can contribute to developing sophisticated and integrated systems that meet the desired performance objectives.
06) Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA):
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) is a critical skill for mechanical design engineers. It involves designing products emphasizing ease of manufacturing, assembly, and maintenance. Engineers can minimize costs, reduce production time, and enhance product quality by considering manufacturing processes, assembly techniques, and material selection early in the design phase. DFMA principles ensure that designs are optimized for efficient manufacturing, minimizing the risk of errors, rework, and delays. By incorporating DFMA principles into their design approach, mechanical design engineers can create designs that are not only innovative and functional but also practical and cost-effective.
07) Knowledge of Codes, Standards, and Regulations:
Mechanical design engineers must be well-versed in the relevant codes, standards, and regulations applicable to their industry. Knowledge of Codes, Standards, and Regulations includes safety regulations, design guidelines, and industry-specific standards. Understanding and adhering to these regulations ensures that the designed products meet the required quality, safety, and performance criteria. Keeping up-to-date with the latest codes and standards is crucial for mechanical design engineers to design products that comply with legal and industry requirements, providing peace of mind to clients and end-users.
08) Effective Communication and Collaboration:
Strong communication and collaboration skills are essential for mechanical design engineers to work effectively in cross-functional teams. Design engineers must be able to articulate their design concepts, present their ideas, and effectively communicate with stakeholders, including clients, manufacturers, and other team members. Listening actively, understanding requirements, and incorporating feedback are crucial for successful collaboration. Effective communication and collaboration foster efficient teamwork, minimize misunderstandings, and ensure that design objectives are met. Mechanical design engineers who excel in communication and collaboration can navigate complex projects and foster productive relationships, ultimately leading to successful design outcomes.
09) Creativity, Innovation, and Problem-Solving:
Mechanical design engineering demands a creative and innovative mindset. The ability to think outside the box, generate novel ideas, and develop unique design solutions is invaluable. Design engineers need to balance functionality, aesthetics, and feasibility while pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Cultivating creativity through continuous exploration, brainstorming, and exposure to diverse design concepts fosters innovation and drives breakthrough solutions. Harnessing your creativity as a mechanical design engineer enables you to design technically sound, visually appealing, and user-friendly products.
Problem-solving skills are at the core of mechanical design engineering. Design engineers encounter various challenges, from structural issues to performance optimization and manufacturability constraints. The ability to analyze problems, break them down into manageable components, and develop practical solutions is essential. Employing analytical thinking, computational tools, and engineering principles, design engineers tackle design challenges head-on. Strong problem-solving skills enable engineers to identify potential issues early in the design phase, implement robust solutions, and ensure the functionality and reliability of the final product.
10) Continuous Learning and Adaptability:
The field of mechanical design engineering is continuously evolving, with advancements in technology, materials, and design methodologies. Mechanical design engineers must embrace a mindset of continuous learning and adaptability to stay current and thrive in this dynamic field. Engaging in professional development activities, attending conferences, and staying abreast of industry trends and emerging technologies is essential. By continuously expanding their knowledge base and being open to learning, mechanical design engineers can enhance their skill sets, explore new design approaches, and remain at the forefront of innovation.
Conclusion:
Becoming a skilled mechanical design engineer requires technical expertise, creativity, problem-solving abilities, and effective communication. By mastering the ten essential skills discussed in this article, aspiring mechanical design engineers can position themselves for success in this specialized field. From technical proficiency and CAD expertise to creativity and continuous learning, these skills empower design engineers to develop innovative, functional, and manufacturable designs. Embrace these skills, invest in your professional development, and embark on a journey of growth and achievement as a mechanical design engineer.
How to Become a Mechanical Design Engineer in 24 Weeks – A step by step Guide
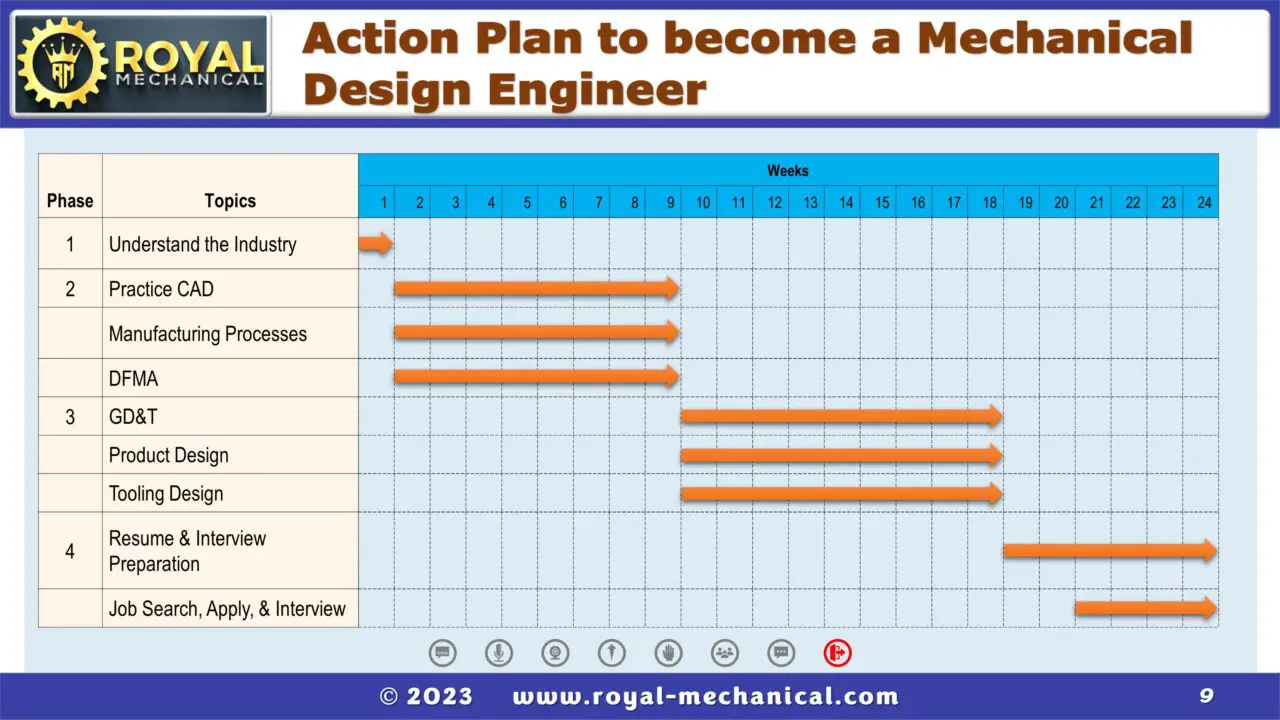
Step-1) Understand the Industry
Understand the Industry by finding Answers to Following Questions
- 1a) What kind of jobs are available in a company?
- 1b) What industries are related to the mechanical engineering domain?
- 1c) What kind of companies are there in the mechanical Industry?
- 1d) What kind of departments are there in a company which employs mechanical engineers?
- 1e) What designations are available for mechanical engineers within these departments?
- 1f) What are the roles and responsibilities of mechanical engineering designations within these departments?
- 1g) What are the educational qualifications, skills, and experience required for a mechanical engineer to be recruited for these positions/designations?
- 1h) Above all, what are the high-salaried jobs?
Step-2) Practice CAD: Practice CAD to gain Proficiency.
- 2a) Part Design
- 2b) Sheet Metal Design
- 2c) Assembly Design
- 2d) Manufacturing Drawing Creation
Step-3) Understand Manufacturing Processes
Study Real Life parts and assemblies to understand the Manufacturing Processes of below most widely used products
- 3a) Machined Products
- 3b) Sheet Metal Products
- 3c) Plastic Products
Step-4) Understand Principles of Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
Study Real Life parts and assemblies to understand the Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
- 4a) Machined Products
- 4b) Sheet Metal Products
- 4c) Plastic Products
Step-5) Understand Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
Understand 14 Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) and their applications with examples.
I) Tolerances of FORM
- 1) Straightness
- 2) Flatness
- 3) Circularity
- 4) Cylindricity
II) Tolerances of PROFILE
- 5) Profile of a Line
- 6) Profile of a Surface
III) Tolerances of ORIENTATION
- 7) Angularity
- 8) Perpendicularity
- 9) Parallelism
IV) Tolerances of LOCATION
- 10) Position
- 11) Concentricity
- 12) Symmetry
V) Tolerances of RUN-OUT
- 13) Circular Run-out
- 14) Total Run-out
Step-6) Create Product Designs using CAD software.
Design Real-Life Products of the below items (a project-oriented approach)
- 6a) Machined Products
- 6b) Sheet Metal Products
- 6c) Plastic Products
- 6d) Weldment Products
Step-7) Create Tooling Designs using CAD software.
Design Real-Life Tooling of the below items (a project-oriented approach)
- 7a) Jigs
- 7b) Fixtures – Machining, Welding, Checking
- 7c) Press Tools / Stamping Dies – Shearing, Bending, Forming
- 7d) Plastic Injection Moulds
Step-8) Prepare an Effective Resume and Prepare for an Interview
- 8a) Prepare an effective resume and cover letter for job roles and create profiles on job portals.
- 8b) Prepare for interview questions and answers.
Step-9) Job Search, Apply, and Interview
- 9a) Search for jobs on job portals
- 9b) Apply for jobs.
- 9c) Not Just Attend. Succeed in job interviews. Remember, You have prepared for success.
FAQs
What are the essential skills required to become a mechanical design engineer?
Essential skills for a mechanical design engineer include Technical and Domain Proficiency, Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T), Knowledge of Materials and Manufacturing Processes, Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA), and Knowledge of International Standards.
Why are Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing crucial for mechanical design engineers?
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is crucial for mechanical design engineers as it provides a standardized language for communicating design specifications and tolerances on engineering drawings. GD&T ensures precise definition of form, orientation, and location of features, enabling accurate manufacturing and assembly. Proficiency in GD&T reduces ambiguity, improves design clarity, and facilitates effective communication between design engineers and manufacturing teams. It ensures consistency, interchangeability, and quality in production, resulting in functional and reliable products. GD&T enhances design engineers’ ability to convey design requirements, ensures compliance with industry standards, and contributes to the overall success of the design and manufacturing process.
What is the significance of Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) in mechanical design engineering?
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) is significant in mechanical design engineering as it optimizes product designs for efficient manufacturing and assembly processes. By considering manufacturing constraints and assembly requirements early in the design phase, engineers can reduce production costs, minimize assembly time, improve product quality, and enhance overall manufacturability. DFMA principles enable engineers to simplify designs, eliminate unnecessary complexity, select appropriate materials, and ensure compatibility with existing manufacturing capabilities. By incorporating DFMA practices, mechanical design engineers can streamline the production process, increase productivity, and deliver cost-effective, high-quality products to market.
How can I improve my technical proficiency as a mechanical design engineer?
Improve technical proficiency by continuous learning: study core engineering principles, take online courses, engage in hands-on projects and internships, join engineering societies, stay updated with industry trends, attend workshops/conferences, and actively participate in professional development opportunities.
Which CAD software should I learn to enhance my design engineering skills?
Learn CAD software like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or CATIA. SolidWorks offers comprehensive 3D modeling and simulation capabilities. AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and detailing. CATIA is famous for complex surface modeling and assembly design, especially in the aerospace and automotive industries. Consider industry preferences and project requirements to determine the most appropriate software for your career growth.
How important is creativity in the field of mechanical design engineering?
Creativity is essential in mechanical design engineering. It enables engineers to think innovatively, generate unique solutions, and push the boundaries of traditional designs. Creative approaches lead to more efficient, functional, and visually appealing products. It fosters innovation, differentiation, and competitive advantage. By embracing creativity, design engineers can tackle complex challenges, optimize designs, and deliver groundbreaking solutions that meet user needs and exceed expectations.
What role does problem-solving play in the daily work of a mechanical design engineer?
Problem-solving is integral to the daily work of a mechanical design engineer. They encounter various challenges, from design constraints to performance issues. Problem-solving skills allow engineers to analyze problems, identify root causes, and develop practical solutions. It involves critical thinking, logical reasoning, and utilizing engineering principles. By applying problem-solving techniques, design engineers can overcome obstacles, optimize designs, ensure functionality, and meet project objectives, leading to successful and efficient outcomes.
Why is knowledge of materials and manufacturing processes important for mechanical design engineers?
Knowledge of materials and manufacturing processes is crucial for mechanical design engineers as it enables informed decision-making throughout the design process. Understanding materials allows engineers to select the most suitable options based on properties, strength, durability, and cost. Knowledge of manufacturing processes ensures designs are optimized for production, considering feasibility, efficiency, and quality control. This knowledge enhances product performance, manufacturability, and cost-effectiveness, leading to successful designs that meet customer requirements and industry standards.
How does mechanical systems integration contribute to the success of a design engineer?
Mechanical systems integration is vital for design engineers as it ensures the seamless coordination and compatibility of various system components. Design engineers can optimize system performance, enhance reliability, and meet functional requirements by integrating different subsystems and components. Effective integration minimizes conflicts, inefficiencies, and performance issues. It requires a holistic perspective, collaboration with other engineering disciplines, and proactive identification of potential conflicts. By addressing integration challenges early on, design engineers can make necessary adjustments, reduce rework, and achieve a cohesive, reliable, and optimized final product.
How can effective communication and collaboration skills benefit mechanical design engineers?
Effective communication and collaboration skills benefit mechanical design engineers in multiple ways. First, they allow engineers to articulate design concepts, understand client requirements, and align project objectives. Collaboration fosters teamwork, encourages diverse perspectives, and promotes knowledge sharing, leading to innovative design solutions. Effective communication with cross-functional teams and stakeholders ensures smooth project execution, minimizes misunderstandings, and facilitates the incorporation of feedback. Finally, it enables design engineers to work seamlessly with manufacturing, procurement, and quality control teams, resulting in well-coordinated and successful design implementation. Strong communication and collaboration skills ultimately enhance productivity, foster efficient project execution, and contribute to the overall success of mechanical design engineers.
Why are continuous learning and adaptability crucial for mechanical design engineers?
Continuous learning and adaptability are crucial for mechanical design engineers as the field constantly evolves with technological advancements, materials, and design methodologies. Engineers can acquire new skills, stay abreast of industry trends, and explore innovative design approaches by staying updated and continuously learning. Adaptability allows engineers to embrace change, tackle new challenges, and adjust to evolving project requirements. It enables them to integrate emerging technologies, adopt new design tools, and respond to market demands. Continuous learning and adaptability foster professional growth, enhance problem-solving abilities, and enable engineers to deliver cutting-edge designs that meet the industry’s and clients’ ever-changing needs.
Related Article: